 Yellow
Sack Spider
Yellow
Sack Spider
|
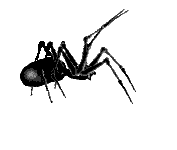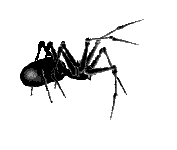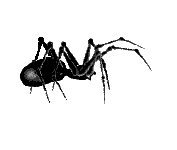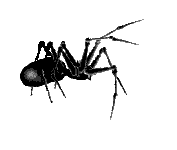
The yellow sac is widely distributed across world. It is often shipped in agricultural products such as grapes and can make its way into homes on produce. Found from central Europe to central Asia, most of North, Central and South America and Africa. It is the cause of a lot of spider bites and other unwanted encounters. A lot of house spiders are killed on suspicion on being yellow sac spiders which may seem a bit unfair. It takes shelter in flattened silk tubes during the day and moves about to hunt during the night. It often lives in houses and can frequently be found crawling upon walls or other vertical surfaces. The prey is a wide diet of arthropods, including spiders larger than themselves and even their own eggs. The spider does not produce webs. Instead they construct sacs in protected areas. The idea of creating sacs instead of webs has given the Yellow Sac Spider its name. Around 30 percent of adult males get killed and consumed by females at mating. The yellow sac spider is about a quarter-inch long, and beige or pale yellow in colour. It does not have distinguishing markings, but its front legs are longer than the rest of its legs. The chelicerae of yellow silk spiders are very powerful, and the fangs can penetrate human skin quite easily. Most bites on humans occur when people are gardening or performing other kinds of outdoor activities. The venom has mild and local cytotoxic and neurotoxic effects. No fatal incidents from encounters with the yellow sac spider have ever been recorded. Bites from a the yellow sac spider are often misinterpreted as bites from a brown recluse spider. The symptoms and the development of the wound are quite the same but less severe. However the bite is quite painful from the outset. One should seek medical treatment immediately after a bite. A person usually develops redness, swelling, and itching near the site of the bite. Redness disappears after about 72 hours and the skin heals in a week or two. |


